Getting Started¶
Why worrying about the low-level of blockchain technology, and having to worry about building your network when you can leverage the benefits of the technology without having to know the details of its operation. TrustOS abstracts all the complexity of blockchain technology implementing the basic operations you need to leverage the power of blockchain technology.
We have created several APIs for tracking the whole lifecycle of assets, for creating and managing transferable tokens, for offering agreement between diferent parts and ensuring confidence and integrity in the all the generated information.
Before starting, it may be interesting for you to know about the architecture and the different modules that compound TrustOS.
Login¶
In order to use the APIs, you need to have an active user and login to use the system. Every API has a login method, which asks for a user and password.
Login UI¶
To facilitate the first interactions with TrustOS there is a login website so that the user can easily login and authenticate the next use of the website through cookies that contains the JWT and that expires after the JWT becomes invalid.
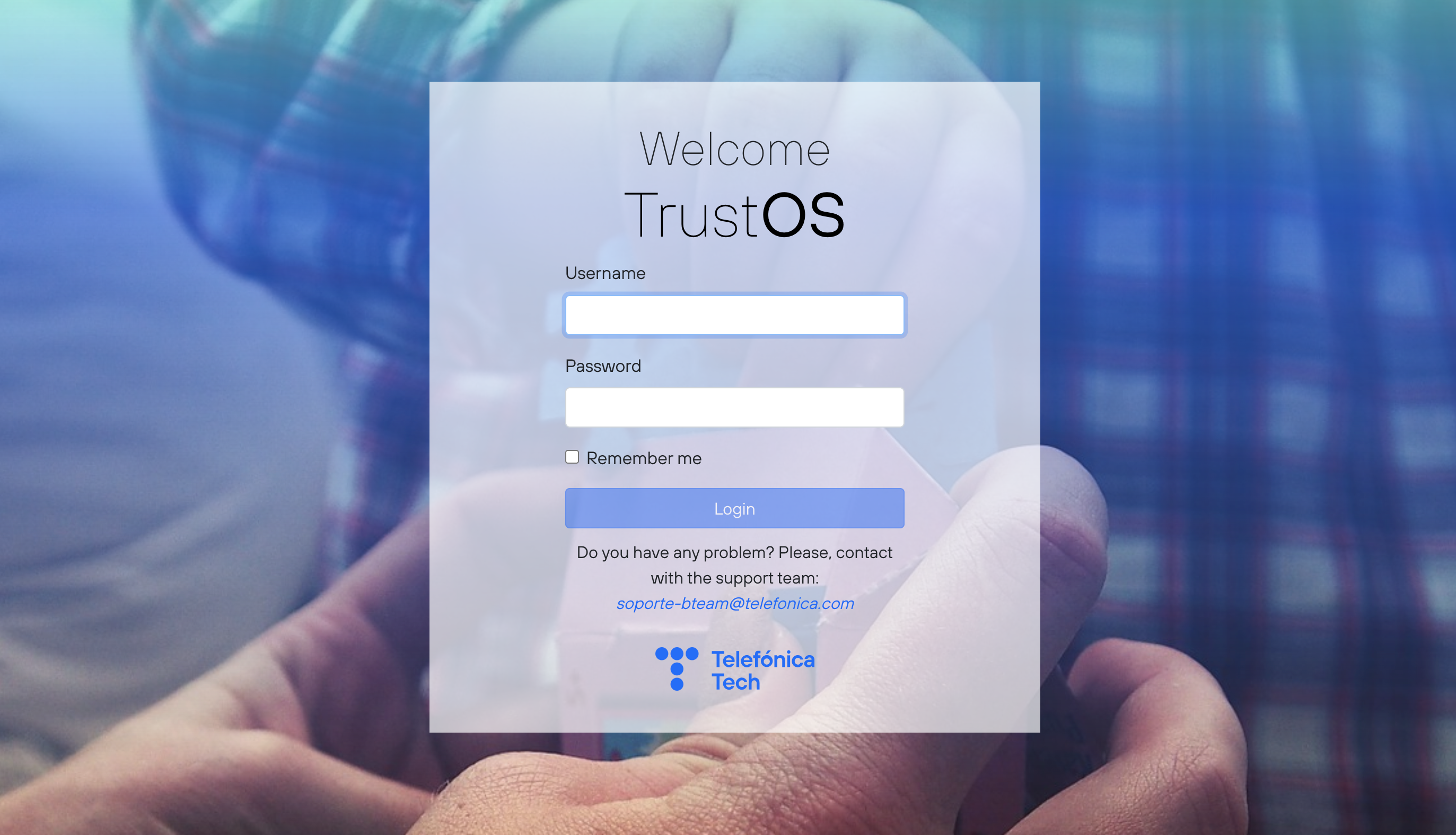
Login request¶
Once your solution has matured, it would be nice to integrate the login process through API requests.
A call to the login method will return a JWT token, of this form:
{
"message": "eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJ1c2VyIjoidGVzdCIsImV4cCI6MTU2MDAwMDE5MH0.M4PBSslERUImcOpWgg--N-2ZNW306BzWXTZVJgtdXWE"
}
Choose an API and start developing¶
Once the login is sucessfully done it is time to start developing your own solution based on one of the TrustOS modules.
Swagger UI¶
We have created a simple website that aggregates all the accesible modules so that the user can easily reach and test all the functionalities.
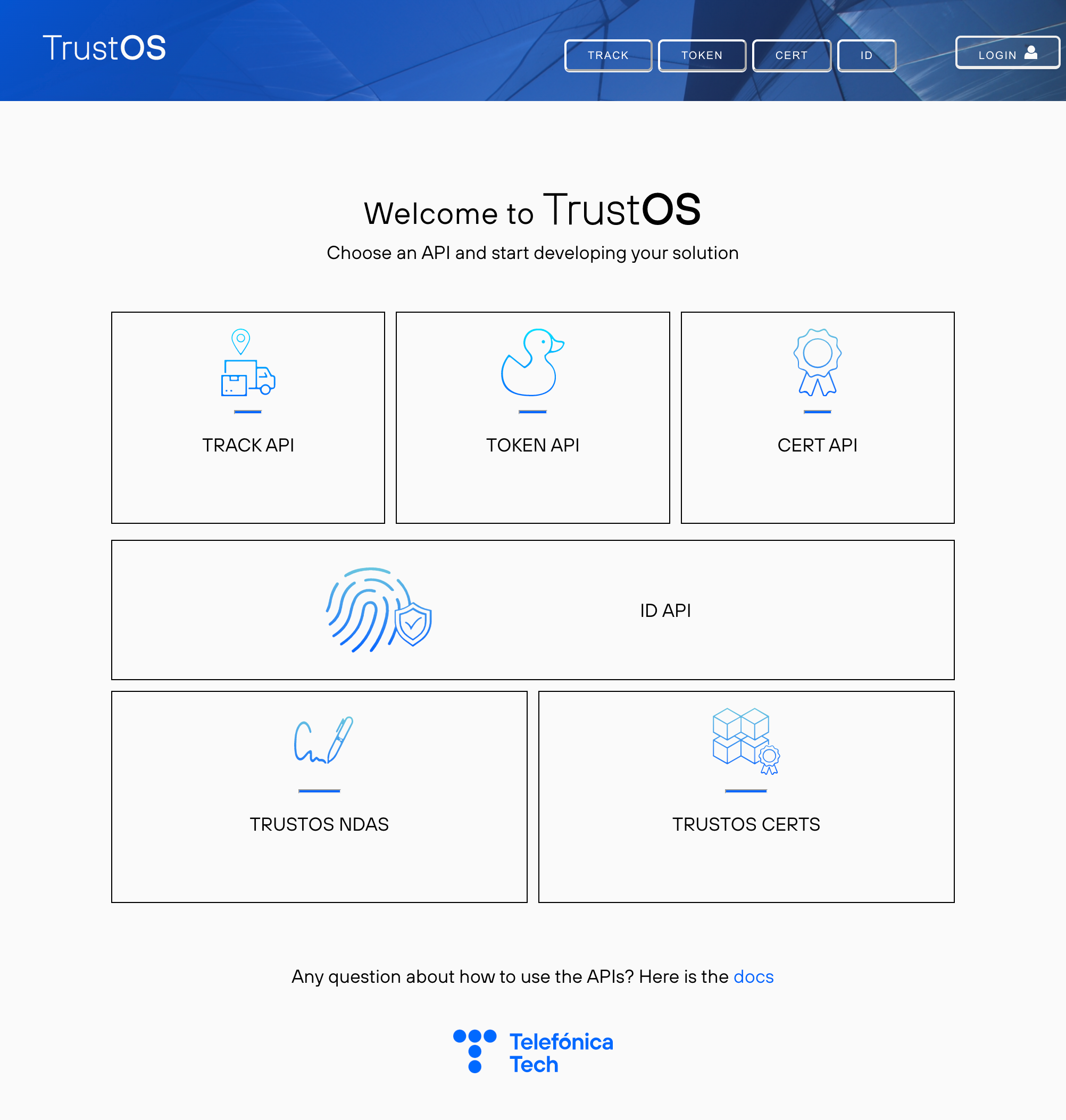
If you have login using the Login UI, it is simple to see and copy the JWT Token just clicking the header green button JWT.
Choose an API to see what there is inside and then you have to click the button Authorize, on the right of the screen.
From there, in the “value” field of ApiKeyAuth, you should write “Bearer” followed by the JWT Token already copied:
Bearer eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJ1c2VyIjoidGVzdCIsImV4cCI6MTU2MDAwMDE5MH0.M4PBSslERUImcOpWgg--N-2ZNW306BzWXTZVJgtdXWE
You should now see that all the locks in swagger are closed, meaning that you are now authenticated!
API request¶
Every call to the API, has to be authenticated, so the caller must provide this message as proof of his identity.
Add the following header to your HTTP request in order to authenticate your call:
Bearer eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJ1c2VyIjoidGVzdCIsImV4cCI6MTU2MDAwMDE5MH0.M4PBSslERUImcOpWgg--N-2ZNW306BzWXTZVJgtdXWE
Attention
Please make sure you write "Bearer" before the JWT token
If you are calling the APIs from Postman, you can set manually the headers (you can see an example in tutorials section):
{
"Authorization": "Bearer eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJ1c2VyIjoidGVzdCIsImV4cCI6MTU2MDAwMDE5MH0.M4PBSslERUImcOpWgg--N-2ZNW306BzWXTZVJgtdXWE"
}
Now it is time to read more about the TrustOS modules.